Symptoms and causes of neurofibromatosis
Neurofibromatoses are a group of genetic disorders that cause tumors in the nervous system. There are three types of neurofibromatosis: mainly neurofibromatosis 1 (NF1), neurofibromatosis 2 (NF2), and schwannomatosis. The symptoms are usually mild but may cause serious complications. Here are the common symptoms of neurofibromatosis and what causes them.
Symptoms
The common signs and symptoms of neurofibromatosis are as follows:
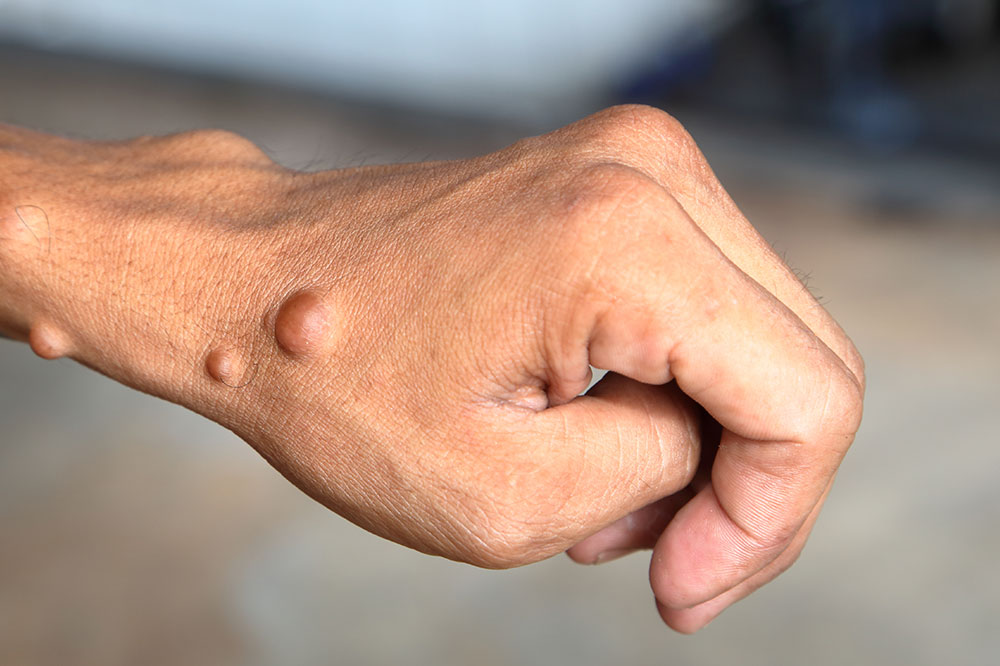
- Small bumps on and under the skin
These tumors tend to grow inside the body; however, sometimes, they may even grow under the skin. When these growths are present in the nerves, they may result in disfiguration of the face. These bumps called Neurofibromas may also increase in number with age.
- Learning disabilities
Children affected by the NF1 gene may find their thinking abilities impaired. They may find it difficult to read or perform mathematics. Moreover, the child may also experience ADHD or a speech delay.
- Light brown spots
Harmless brown spots called cafe au lait spots occur on the skin. Usually, the presence of more than six of these spots indicates NF1. They occur during childbirth or the initial years and stop after childhood.
- Other bumps and freckles
Bumps called Lisch nodules are commonly noticed in the iris of the eyes. They are painless. Also, freckles occurring in various body folds, especially in areas like the armpits and the groin, are also common.
- Problems with the ears
NF2 may result in the development of slow-growing tumors in the ears. They may also grow on the nerves that carry sound to the brain. As a result, one may experience symptoms such as hearing loss, ringing in the ears, and loss of balance.
Causes
The following reasons are responsible for the development of neurofibromatosis.
- NF1
The NF1 gene, located on chromosome 17, creates a protein called neurofibromin that helps regulate the growth of cells. A mutation in this gene causes neurofibromin to deplete, allowing cells to grow uncontrollably.
- NF2
The NF2 gene produces a protein called merlin, which suppresses the formation of tumors in the body. Mutations occurring in these genes cause a loss of merlin, resulting in an uncontrolled development of cells. - Schwannomatosis
The NF1 and NF2 genes cause schwannomatosis, which causes tumors to grow on the cranial, spinal, and peripheral nerves. Nevertheless, these tumors rarely grow on the nerves that carry sound to the brain, leading to sound loss of lower intensity.


